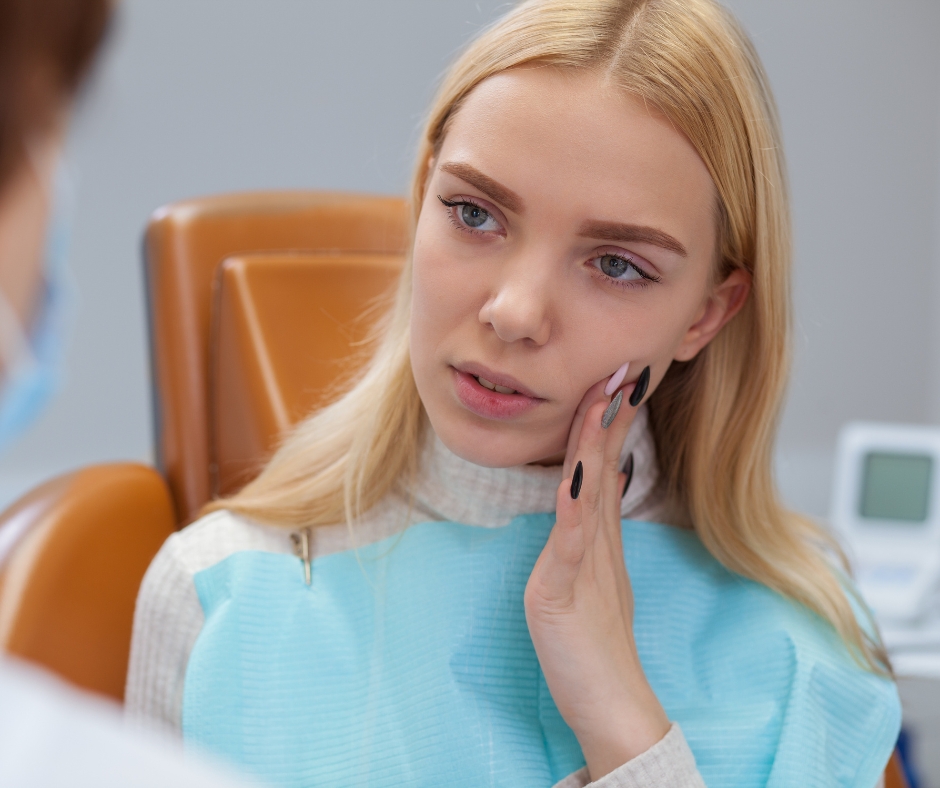
Tooth infections, also known as dental abscesses, can be painful and potentially serious. These infections occur when bacteria invade the pulp of the tooth or the surrounding tissues. While proper dental care and treatment are essential to address the underlying cause of the infection, antibiotics can play a crucial role in managing the infection and preventing its spread. So, what is the best antibiotic for a tooth infection? Let’s explore the options and considerations when it comes to choosing the right antibiotic.
Understanding Dental Infections: A Multi-Faceted Challenge
Dental infections can vary in severity, ranging from localized abscesses to more widespread infections that can impact the surrounding tissues. The choice of antibiotic depends on factors such as the type of bacteria causing the infection, the patient’s medical history, and the severity of the infection.
Common Antibiotics for Dental Infections:
- Penicillin: Penicillin and its derivatives, such as amoxicillin, are often considered the first-line antibiotics for dental infections. They are effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria commonly associated with dental abscesses.
- Clindamycin: In cases of penicillin allergy or when the infection is resistant to penicillin, clindamycin is an alternative antibiotic option. It’s effective against certain bacteria and can be prescribed when necessary.
- Metronidazole: This antibiotic is often used in combination with other antibiotics to target anaerobic bacteria commonly found in oral infections.
- Augmentin (Amoxicillin/Clavulanate): This combination antibiotic is sometimes prescribed for dental infections that may require a broader spectrum of coverage.
Individualized Treatment: The Role of Dentists
It’s important to note that the best antibiotic for a tooth infection can vary from person to person. Dentists play a crucial role in determining the appropriate antibiotic based on factors such as the patient’s medical history, any allergies they may have, and the specific bacteria causing the infection. Proper diagnosis and assessment by a dental professional are essential to ensure effective treatment.
Dosage and Duration:
The dosage and duration of antibiotic treatment for a tooth infection are determined by the severity of the infection and the specific antibiotic prescribed. It’s vital to follow your dentist’s instructions carefully, even if the symptoms begin to improve. Completing the full course of antibiotics helps prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Remember: Antibiotics are Not a Substitute for Dental Treatment:
While antibiotics can help manage the infection and alleviate symptoms, they are not a substitute for proper dental treatment. Addressing the underlying cause of the infection through dental procedures such as root canal therapy or tooth extraction is crucial for complete resolution.
In conclusion, the best antibiotic for a tooth infection depends on various factors, including the type of bacteria causing the infection and the patient’s medical history. Dentists play a pivotal role in determining the appropriate antibiotic and treatment plan. It’s essential to understand that antibiotics are a part of the treatment process and should be complemented by proper dental care to achieve long-lasting relief and oral health. If you suspect a tooth infection, seek prompt dental attention to receive the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.